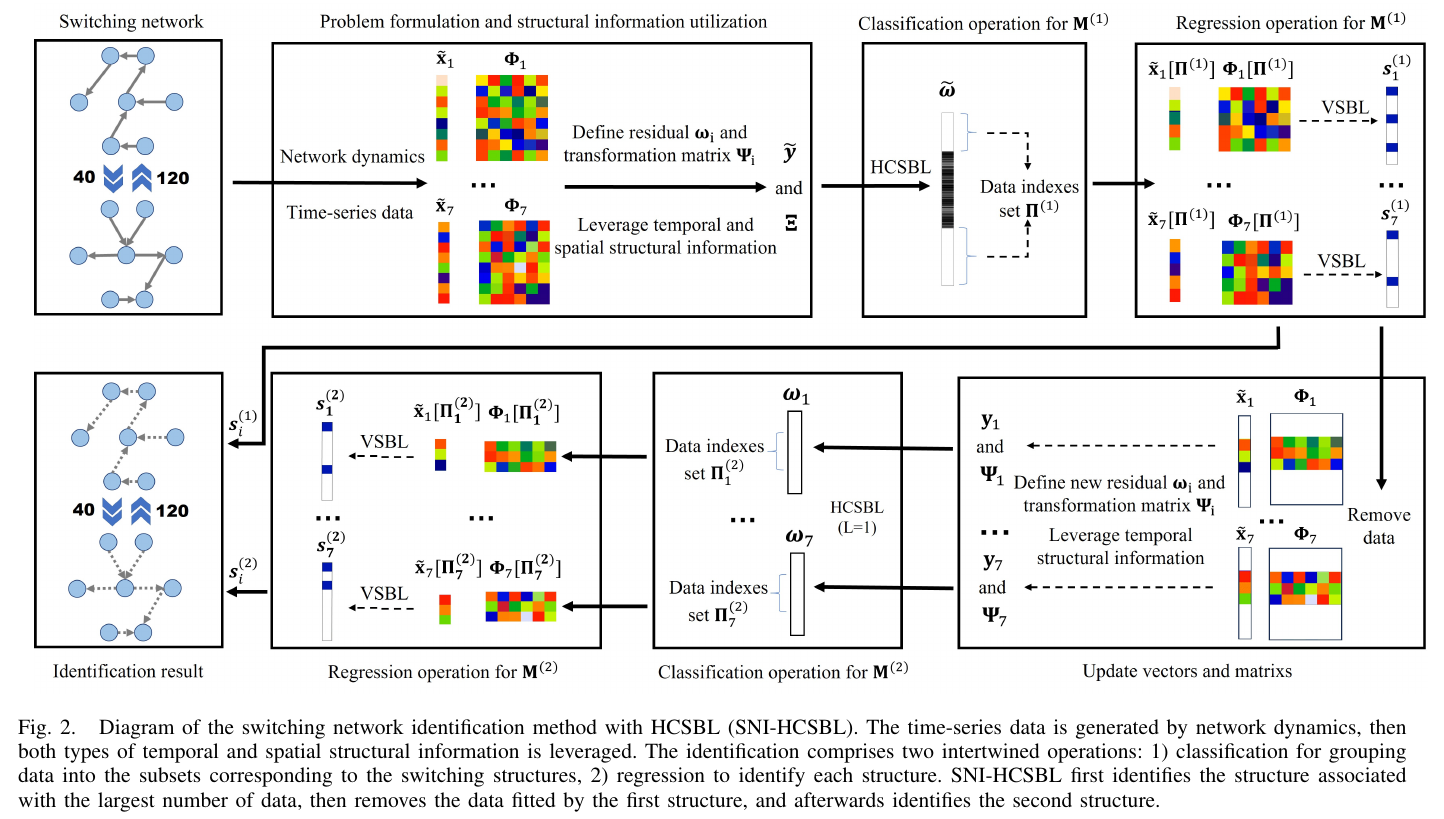
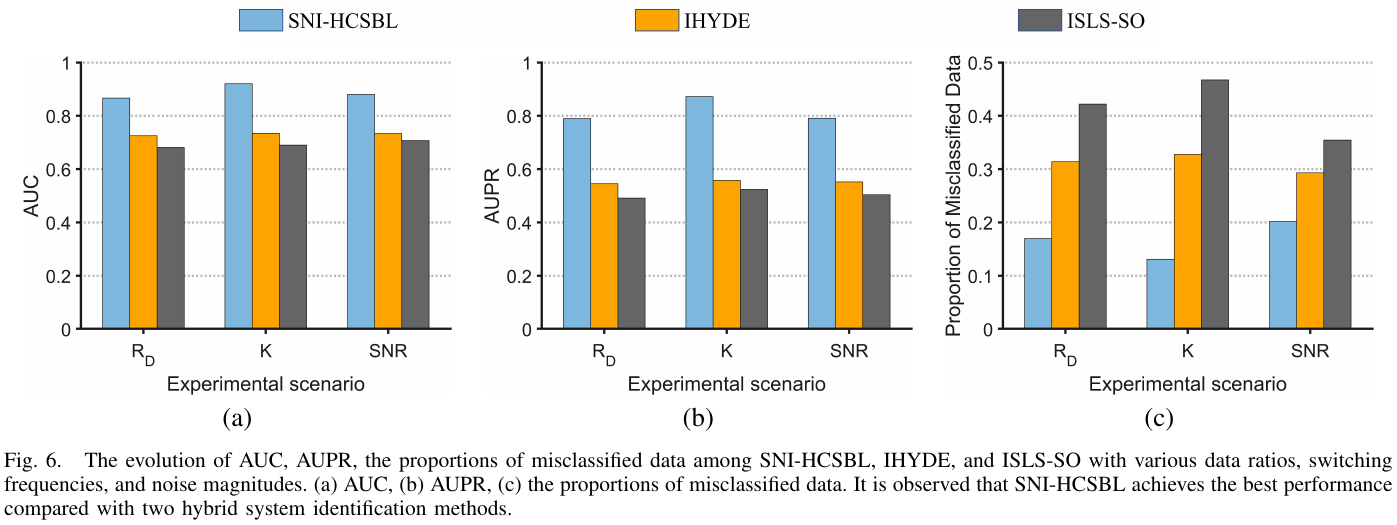
Abstract:Learning dynamical networks based on time series of nodal states is of significant interest in systems science, computer science, and control engineering.Despite recent progress in network identification, most research focuses on static structures rather than switching ones.Therefore, this paper develops an method for identifying the structures of switching networks by exploring and leveraging both temporal and spatial structural information that characterizes the switching process.The proposed method employs a new sparse Bayesian learning algorithm based on coupled hyperblocks to estimate unknown switching instants.Experimental results on benchmark artificial and real networks are elaborated to demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method.