Abstract
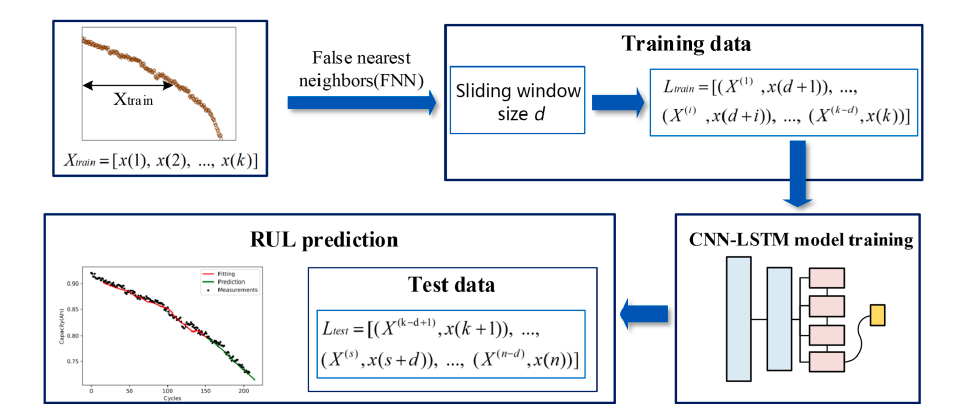
Accurate estimation of the remaining useful life of lithium-ion batteries is critically important for electronic devices. In the existing literature, the widely applied model-based approaches for remaining useful battery life estimation are limited by the complexity of the electrochemical modeling required. In addition, data-driven approaches for remaining useful battery life estimation commonly define unreliable sliding window sizes empirically and the prediction accuracy of these approaches needs to be improved. To address the above issues, use of a hybrid neural network with the false nearest neighbors method is proposed in this paper. First, the false nearest neighbors method is used to calculate the sliding window size required for prediction. Second, a hybrid neural network that combines the advantages of a convolutional neural network with those of long short-term memory is designed for model training and prediction. Remaining useful life prediction experiments for batteries with various rated capacities are performed to verify the effectiveness of the proposed approach, and the results demonstrate that the proposed approach offers wide generality and reduced errors when compared with the other state-of-the-art methods.